

Identify and name groups attached to this chain.Find and name the longest continuous carbon chain.Straight chain alkanes with n>3 is therefor called n-alkanes (n-butane, n-pentane etc.) to pinpoint that they are normal or unbranched.Īlkyl: An alkyl group is an alkane substituent missing one hydrogen, with general formula C nH 2n+1.įor branched alkanes the following rules are given to name them in a way that precisly describes their structure: All isomers have the same general formula C nH 2n+2. The names are obtained by adding the suffix -ane to the Greek root of the number of carbon atoms, prefixes given in the table below.Īlkanes with n>3 can form structural isomers, which means that the carbon chain with a given total carbon number n can be branched in different ways.The simplest alkane compound is methane, with n=1: CH 4 Hydrocarbon: An organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon.Īlkanes which form a chain are called normal, straight chain or unbranched hydrocarbons. Alkanes are also called paraffins.Ĭycloalkane: A one-ring (monocyclic) saturated hydrocarbon, with the general formula C nH 2n. More details about naming of the different classes of organic compounds, functional groups and examples of naming are given in the chapters below.Īlkane: An acyclic saturated hydrocarbon, with the general formula C nH 2n+2. The priority order and the suffixes of the different functional groups are given in the Functional group priority list.

When faced with more than one functional group you simply choose the group with the highest priority as the last name.
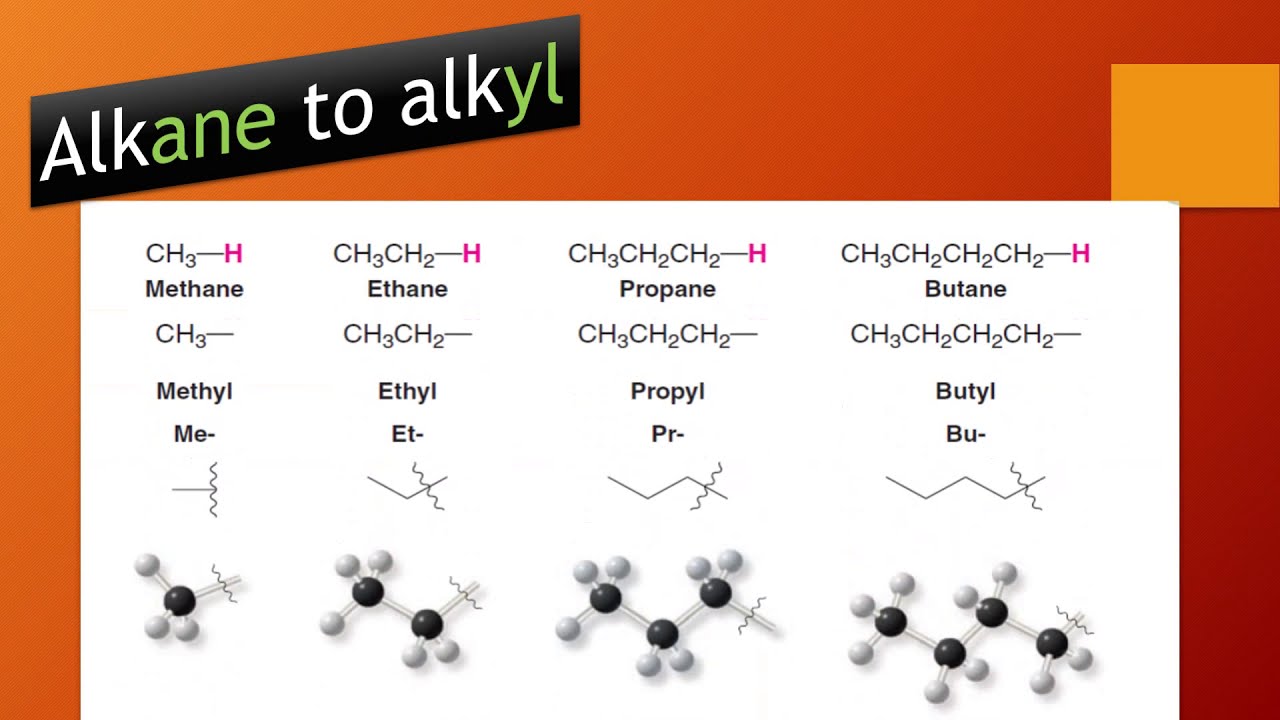
When faced with a single functional group it becomes the last name of the molecule. Prefixes of the different functional groups are given in the Functional group priority list.įunctional groups come in many forms, from the alcohol -OH groups to the carboxyl -CO2H. If many functional groups are present in a molecule, the groups with the lowest priority will be treated as substituents, and prefixes indicating the kind of functional groups are used. When more than one of the same substituent occurs, you have to use a new prefix to designate how many are present as follows:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
