
Xerox Network Systems (XNS) Mailīootstrap Protocol (BOOTP) server also used by Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)īootstrap Protocol (BOOTP) client also used by Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)Īny private dial out serviceĪny private Remote job entry Xerox Network Systems (XNS) authenticationĪny private terminal access Xerox Network Systems (XNS) clearinghouse Xerox Network Systems (XNS) Time Protocol Previously Interface Message Processor logical address management

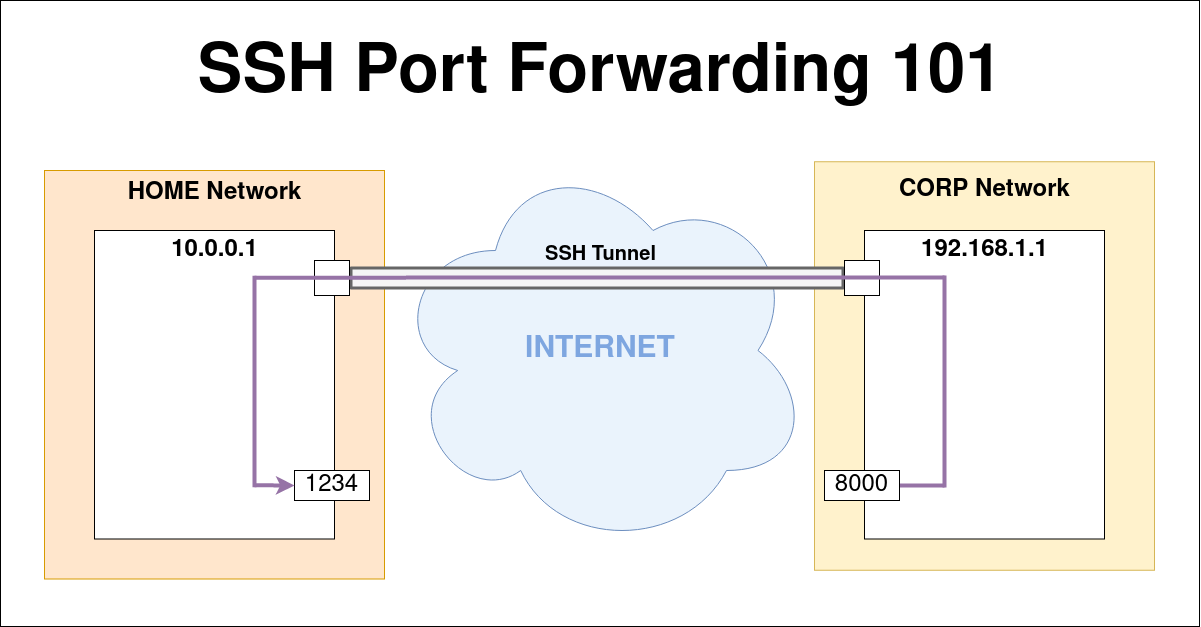
Resource Location Protocol (RLP)-used for determining the location of higher level services from hosts on a network Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP), used for email routing between mail servers Telnet protocol-unencrypted text communications Microsoft EPMAP (End Point Mapper), also known as DCE/ RPC Locator service, used to remotely manage services including DHCP server, DNS server and WINS.Secure Shell (SSH), secure logins, file transfers ( scp, sftp) and port forwarding
BZFLAG PORT FORWARDING SOFTWARE
Used by Unisys Programmer’s Workbench for Clearpath MCP, an IDE for Unisys MCP software development Network Time Protocol (NTP)-used for time synchronizationįormerly Unisys Unitary Login, renamed by Unisys to NXEdit. Network News Transfer Protocol (NNTP)-retrieval of newsgroup messages Ident-Authentication Service/Identification Protocol, used by IRC servers to identify users ISO- TSAP (Transport Service Access Point) Class 0 protocol also used by Digital Equipment Corporation DECnet (Phase V+) over TCP/IPĪCR/ NEMA Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (DICOM) XNS ( Xerox Network Systems) AuthenticationĬI ( Travelport) (formerly Covia) Comms Integratorīootstrap Protocol (BOOTP) Server also used by Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)īootstrap Protocol (BOOTP) Client also used by Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)ĭnsix ( DoD Network Security for Information Exchange) Securit Attribute Token Map XNS ( Xerox Network Systems) Clearinghouse XNS ( Xerox Network Systems) Time Protocol Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP)-used for e-mail routing between mail servers Secure Shell (SSH)-used for secure logins, file transfers ( scp, sftp) and port forwarding Programming technique for specifying system-allocated (dynamic) ports On Unix-like operating systems, a process must execute with superuser privileges to be able to bind a network socket to an IP address using one of the well-known ports. They are used by system processes that provide widely used types of network services. The port numbers in the range from 0 to 1023 are the well-known ports or system ports. Multiple applications are known to use this port. Port is not registered with IANA for the application Port is registered with IANA for the application

However, many unofficial uses of both well-known and registered port numbers occur in practice. The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) is responsible for maintaining the official assignments of port numbers for specific uses. They usually use port numbers that match the services of the corresponding TCP or UDP implementation, if they exist. Stream Control Transmission Protocol (SCTP) and Datagram Congestion Control Protocol (DCCP) also use port numbers. The even-numbered ports were not used, and this resulted in some even numbers in the well-known port number range being unassigned. Later, Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and User Datagram Protocol (UDP) needed only one port for bidirectional traffic (full duplex). Originally, port numbers were used by the Network Control Program (NCP) which needed two ports for half duplex transmission. This is a list of Internet socket port numbers used by protocols of Transport Layer of the Internet Protocol Suite for the establishment of host-to-host connectivity.

List of TCP and UDP port numbers from 0 to 1023


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
